In the world of forensic science, precision and accuracy are non-negotiable. One of the most groundbreaking tools aiding a crime scene investigator today is photogrammetry software—a digital solution that turns photographs into accurate 3D models of crime scenes. This technology provides a clearer perspective, helping investigators analyze, document, and present evidence with enhanced accuracy and speed.
What is Photogrammetry Software?
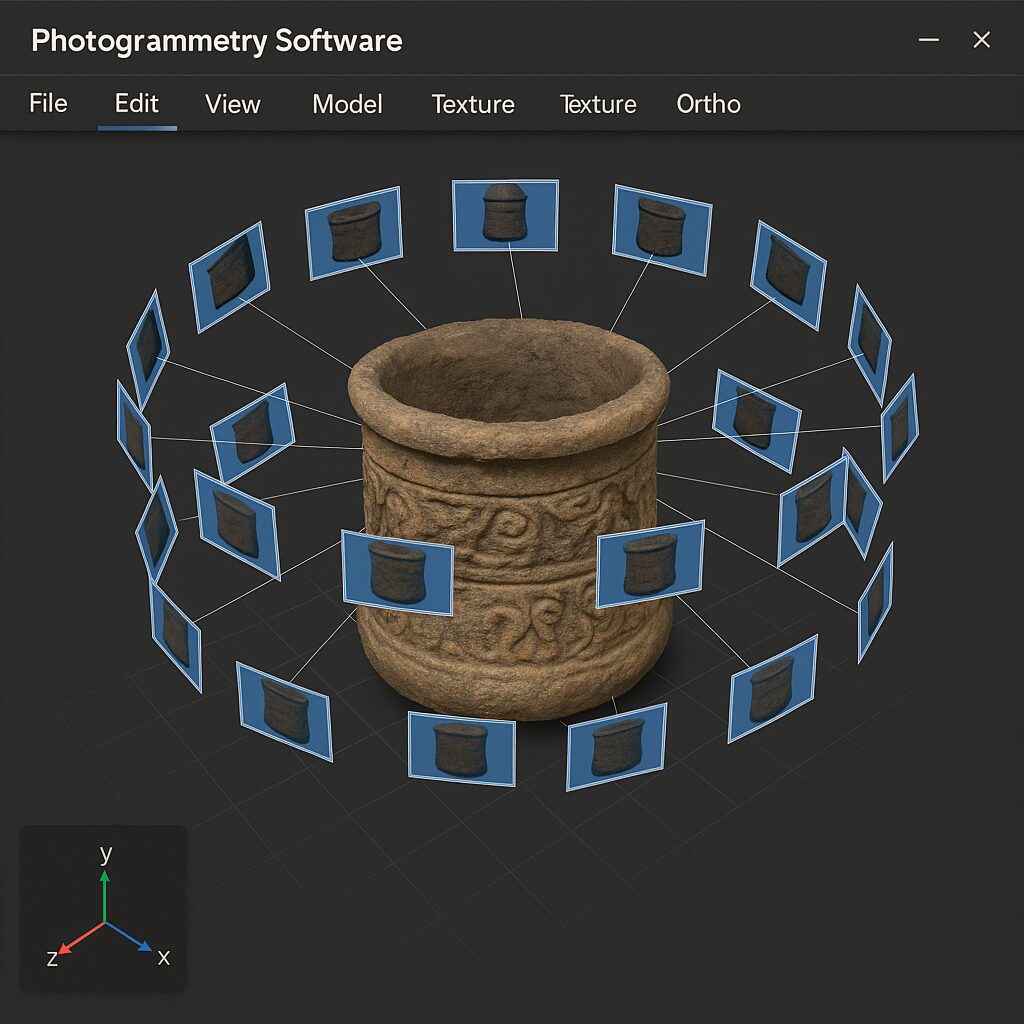
Photogrammetry software uses overlapping images taken from different angles to generate detailed, scaled 3D models or 2D maps of real-world environments. In a forensic setting, this means capturing a scene as it was at the time of the incident—without disturbing physical evidence.
By integrating multiple photographs, the software creates a spatially accurate reconstruction. This virtual environment can be explored, measured, and even revisited long after the actual scene has been cleared.
Why Crime Scene Investigators Rely on Photogrammetry
1. Accurate Scene Reconstruction
A crime scene investigator needs to document the layout and positioning of physical evidence precisely. Traditional hand measurements leave room for human error, but photogrammetry offers high-accuracy 3D reconstructions. This allows investigators to:
- Analyze spatial relationships between objects
- Pinpoint trajectories and lines of sight
- Validate or challenge eyewitness accounts
2. Time-Efficient Documentation
Manual sketches and note-taking are time-consuming. Photogrammetry speeds up the process by capturing the scene in minutes using high-resolution photographs. Investigators can later generate multiple views and perspectives, ensuring that no critical detail is missed.
3. Enhanced Courtroom Presentations
Presenting physical evidence in court is often limited by traditional photographs and charts. Photogrammetry adds immersive 3D visuals, making it easier for jurors to understand complex crime scenes. This technology boosts transparency and can significantly support legal arguments by providing factual, visual representations.
How It Works: From Field to Forensics Lab
Step 1: Capture
The crime scene investigator photographs the area from various angles, ensuring ample overlap between images. High-quality digital cameras and drones are often used for aerial shots or large-scale scenes.
Step 2: Process
These images are uploaded to photogrammetry software, which analyzes the overlapping points and calculates spatial data. The software then stitches the images into a 3D model or orthomosaic map.
Step 3: Analyze
Once processed, investigators can:
- Measure distances and angles with precision
- Highlight specific evidence
- Share models with colleagues or legal professionals for review
Conclusion
Photogrammetry software is revolutionizing how crime scene investigators operate. From faster data collection to reliable courtroom visuals, this technology provides critical support in the quest for justice. As the demand for precision grows, adopting digital tools like photogrammetry is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity.
FAQs
Q1: Is photogrammetry software difficult to use for new investigators?
A1: Most modern photogrammetry tools come with intuitive interfaces. While training is recommended, users can often achieve usable results with minimal learning.
Q2: Can this technology replace manual scene sketches?
A2: While traditional methods are still used, photogrammetry significantly reduces the need for manual sketches by offering high-detail digital representations.
Q3: What types of crime scenes benefit most from photogrammetry?
A3: All types—indoor, outdoor, vehicular accidents, and homicides—can be captured with this technology for improved accuracy and analysis.
Q4: Does photogrammetry software support real-time collaboration?
A4: Yes, many tools allow digital sharing of files and remote collaboration between investigative teams and legal professionals.
Q5: How does photogrammetry help in cold case investigations?
A5: Stored models can be revisited and analyzed years later, often revealing new insights or inconsistencies when compared with fresh evidence or theories.